From a long-standing brick-and-mortar model, the healthcare system adopts more virtual care, deepening focus on patient-centricity and engagement.
After many months of the enduring pandemic, taking a brief respite to reflect on the changes that have occurred, and which ones will change the way healthcare is practiced and delivered, is imperative to continue to grow on an individual and system level.
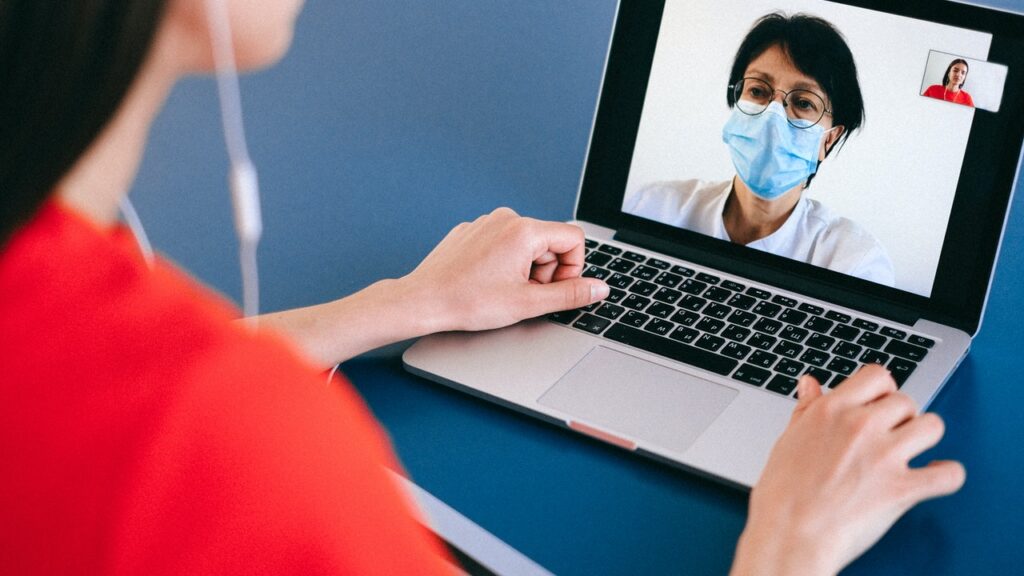
COVID-19 has changed the outlook for healthcare technologies with a renewed focus on telehealth. This is a technology that has been around for quite a while and is only now seeing rapid increased use and adoption due to the physical distancing requirements of the pandemic.
While there are many hurdles in the way of continued implementation of telehealth, one of the biggest hurdles has already been overcome, namely patient and provider buy-in. Since using the technology more frequently and depending on it for appointments during the pandemic, each stakeholder has developed a willingness and interest to use telehealth.

There are many examples of patients and providers realizing the benefit of telehealth in their lives for convenience, efficiency, and even relationship building by enabling a more personal touch in traditionally professional interactions.
For providers specifically, telehealth has provided a range of benefits. The technology allows for remote monitoring, especially of chronic diseases or infections that need frequent check-ups and follow-up visits to keep an eye on the status of disease progression. Virtual visits simplify the disease monitoring process, allowing for physicians to keep a closer eye on the patient with the flexibility of booking frequent appointments, while not constrained by needing to be in-person.
There is also a convenience factor offered by telehealth that, unlike some other industries, physicians have not previously been able to enjoy, namely being able to work from home using a secure platform to conduct online visits.
Telehealth has allowed for further engagement of patients as well as building more personal relationships with patients since interactions tend to be less formal in an at-home setting. This also helps with providing optimal care, allowing doctors, especially in family medicine, to see patients in their home environment and pick up on clues that help with diagnosis and treatment, which may have otherwise gone unmentioned or undiscovered.
From the patient perspective, telehealth adoption was also initially slow before the pandemic however with the recent, rapid and widespread telehealth adoption, patients have also realized its convenience: being able to schedule quick check-ups with physicians in between meetings allows the patient to avoid taking the day off from work, commuting to the doctor’s office, for example – all of which take more time and energy than the actual appointment in most cases. In fact, this may encourage patients who have cut annual physicals out of their health routine, for example, to begin scheduling them again, improving the system of preventative care and the patients’ relationship with healthcare.
This brief exploration of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic has had on the adoption of telehealth is indicative of the larger transformation in healthcare delivery happening now. The healthcare system is moving from a long-standing brick-and-mortar model to one with a large dependence on virtual care, deepening focus on patient-centricity and engagement while using advanced technology to efficiently manage large amounts of high-quality data for optimized patient outcomes. While the past few months have exposed many cracks in the healthcare system, it has also shown the great opportunities that lie ahead for high-quality clinical care.